An Automated Evaluation of Live Forensic Approach
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: Engineering |
| ✅ Wordcount: 3700 words | ✅ Published: 23 Sep 2019 |
AN AUTOMATED EVALUATION OF LIVE FORENSIC APPROACH
ABSTRACT
Live forensics is an enlarging branch of digital forensics that carryout the analysis on live system. The enlightened attack on computer that needs the support of live forensics to discover the evidence because traditional forensics will not gather volatile data. To collect the volatile data we are performing Memory dump, to analyze that it has different plugins and tools. In this part of research we will generate an automation tool which saves the output data in particular file. This paper presents a design to resolve the difficulty by automating the process of acquisition and analyzing the data.
Keywords: Live Forensics, memory dump, live acquisition, live analysis, forensics evidence
- INTRODUCTION
Live Forensics observes the collection of live evidence at the time of a current attack with a limited live investigation. The first point in evidence gathering is the selection of procedure to procure live evidence from a distrust computer. All of the data can help the investigator in finding forensics evidence. The live forensics is the only way to acquire the data but that need to be considered during acquisition is very large and spread over the various locations on a computer. It usually become invariable and time consuming for an investigator to gather the data directly since investigator has informed of multiple tools with their availability and capability to perform a successful live forensics. To acquire volatile data the computer system must be powered on. Volatile data is stored in digital format that has the contents of getting deleted, overwritten or altered[1]. After considering the time complexity and enormous data involved in live forensics the only solution to the problem is to provide a tool that can automate the process of acquiring and analyzing evidence data. This tool can be easily deploy the memory dump and it is capable of maintaining integrity and reliability towards evidence data throughout the process.
- LITERATURE SURVEY
Live forensic methodology allows forensic investigator to run programs on suspect’s system to extract RAM dump and unencrypted files. Random Access Memory commonly known as RAM is the main form of computer storage. In today’s world it is in the form of integrated circuits which stores data and allows the system to access it in any random manner. By stating random it is meant that any data in RAM can be retrieved in a constant time. The other important property of RAM is it stores the data in it only till a power supply exists. Hence it is also referred to as volatile memory.
Despite the fact that power is evacuated, the information put away on the drive isn’t lost in light of the fact that the storage is not unstable unlike volatile memory. Live forensics solves the problems which are able to acquire unencrypted data. To perform live acquisition forensic Investigator must execute code which will run on the CPU of the suspect system. The code will change data in CPU registers and RAM.
This paper represents a design of infraction that reconstructs by memory correlation analysis, and provides a complete design and implementation of memory forensics. The tentative result shows the elucidation that perform multiple memory images correlation analysis based on the extracted memory information. Based on the results, investigators may determine the case occurrence. The proposed design may contribute to cross-platform the digital forensic research and responsible analysis for evidence information.
Three principles to follow during live forensic process:
- Acquire the evidence without damaging the original
- Authenticate the recovered evidence as it is same as the originally seized data
- Analyse the data without modifying content.
In this research, forensics Investigator performs ram dump analysis using volatility framework. Live analysis technique is used to collect the volatile data from RAM. The best way to avoid all these issues is to provide an automation tool that can automate task and provide integrity towards data.
- LIVE FORENSICS
Live forensics acquires data from running systems and provide the information like running processes, Ram dump and system states which cannot be extracted through static forensics. The information extracted from the evidence will be more and accurate of the system’s live condition. Turning off the system may loss the data such as running processes, network connections and mounted file systems. Leaving a running computer may cause evidence to be altered or deleted [3]
The examination of computers to extract evidence within the operating system using sysadmin tools. The investigator needs an appropriate level to access the target system. The investigator deploys and owns the target system and gain access to the user interface and getting the correct responses from the user interface of the system.
Memory acquisition will enable to clean snapshots of memory in the operating system. The responsibility of an forensic investigator is to acquire the evidence about the attacker’s activities when the attack was performed. The investigator will have a control on the system configuration rather than system environment. The best approach to perform live analysis is to hide the live monitoring processes. [6]
Performing live accretion will collect information about the state of running systems and data about running processes as well the files accessed by them. It also acquires the network information which used for to and fro communication from the system.
In live response, the first thing is to collect is the contents from RAM. According to Locard’s Exchange Principle, the contents of RAM first collected so that we can minimize the impact which we have on it. If any other tools run to collect volatile information they are going to be loaded into memory and modify the contents of memory.
3.1 Importance of Live Data Forensics:
RAM contents are fading fastly and investigator cuts the power supply from the system. At that time data will be stored in temporarily in RAM or remotely. All the data is not stored in Hard drive then data will be loss without Live Forensics.[1]
3.2 Benefits of implementing live forensics
- Shortened investigation process.
- Cost efficiency-due to short investigation process.
- Collect better and more evidences.
- Proper acquisition and analysis of volatile data in RAM.
- Quick access to court-admissible evidence.
- Improved chances for successful litigation.
- DEAD FORENSICS
Dead Forensics involves the analysis of a suspect system which is shut down condition through the normal administrative procedures. When the system is in dead state it doesn’t provide the information of any malicious process running on the system, as the system in shut down condition erases the volatile data. The investigator can access the data resides in the system and can analysis on the data available while the system is in offline condition.
If the computer is in switch on condition, then the system has to be turn off by shut down or by either pulling out the power plug. After system shut down the forensic investigator pulls out the hard drive from the system and attaches it as an external media of an forensic system and start the analysis [2]. The forensic investigator will safeguard the evidence that no data tampering may takes place on the external drive. Before starting the analysis the write blocker is used to avoid any type of data tampering, and allows only read access. [7]
4.1 Positive aspects:
1. Forensics is the ability to retrieve hidden and deleted data.
2. No need of overwriting or modifying the evidentiary data obtained from a forensics acquisition
4.2 Limitations:
1. Many unique practical constraints and legal procedure makes the appliance of digital forensics both interesting and complex.
2. As there is a lack of effectiveness in the present forensic investigative techniques which leads to the uncertainties.
3. Investigators need passwords to access the system.
- STATIC ANALYSIS
In static analysis the target system was freeze for analysis of an attached storage media to perform forensic imaging or copy of the system data. For forensic investigative analysis, investigators commonly use open source tools as well as commercial products. Static analysis involves effective recovering data from storage media. It can identify and access all the files on a file system, recover deleted files, locate file using keywords, pattern matches, or modification, access, and creation times. Static analysis methods will extract digital forensic evidence recovery processes and are widely used by legal practitioners. Static analysis can result in an incomplete picture of events. [6]
Static analysis typically provides an investigator with a single snapshot of the storage media. The investigator will not have control over the file system’s state at the time of force shutdown, and the resulting disk state might be inconsistent. Some file systems require additional efforts from the investigator to rectify.
- LIVE FORENSICS ACQUISTION
It considers the retention of volatile data. Investigator will report the chain of custody from the first approaches of computer and determines its power status. To initiate acquisition, the investigator needs to activate the forensics agent and the forensics agent is placed within the kernel space of the computer system giving the forensics investigator administrative rights to the suspect machine.
It was developed in response to the forensic acquisition techniques will retent the volatile data.
To perform the Live Acquisition first disconnect the system from the network to track an active attack, if any damage or loss of valuable information then automatically it will stop [2]. Live forensics will record the time, date, who discovered the problem and how much information was known. Each and every time we must make an note of an situation of what type of actions were taken and what type of results were found. Evidence Forensics will be ready for action to collect information and determine that Action based on the data collected.
Run a network to capture communication flows to and from a compromised system. Tcpdumpraw format will reduce the performance issues. Create a paper copy of data collection and record the results of commands running at the time of data gathering while sending the digital data to a remote host or storing it on external media.
When the computer is powered on, then investigator will collect the data locally, or through the network. The investigator will attach a write blocker system to the suspect machine of a forensic system.
Live forensics may be altered the data and continuously processed. Powering off the system may loss the volatile data like running processes, network connections and file systems.
6.1 Positive aspects:
1. It allows forensics investigators to recover the volatile information to the suspect’s system network settings and shared files and folders.
2. Collects information about the running state of the system.
6.2 Limitations:
1. Data modification during the acquisition process and the dependencies of the forensics acquisition on the suspects system.
6.3 Live forensics process diagram:
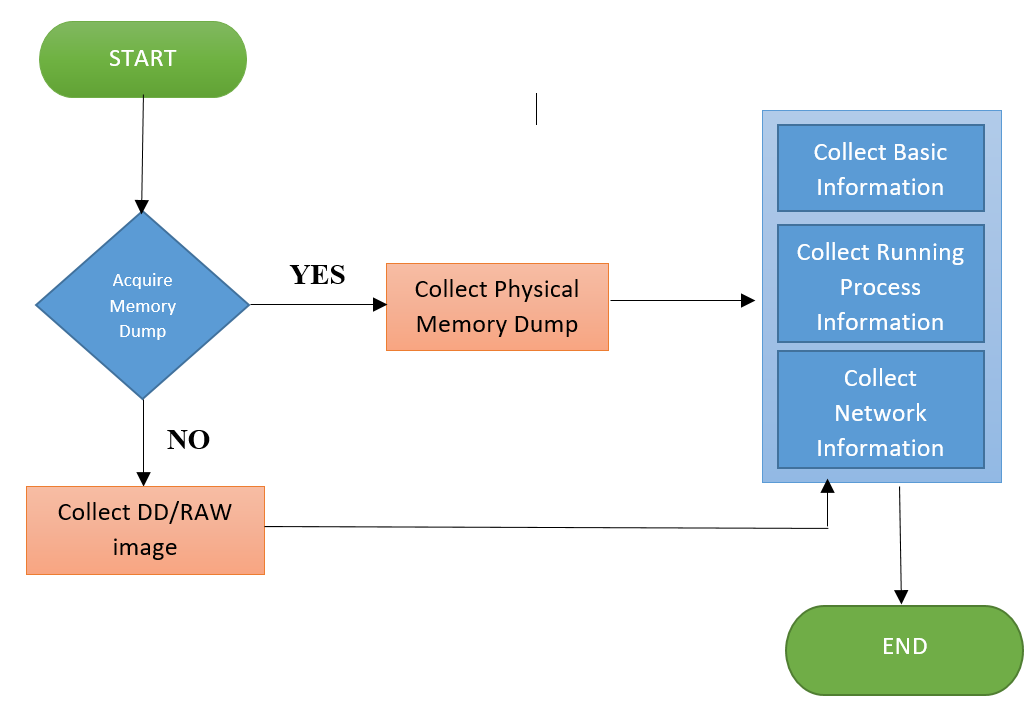
Figure 1: live forensics process
- LIVE FORENSICS ANALYSIS
The ability to collect the information from a RAM often requires information to be gathered from a related non-volatile to analysis, but it may require little acquisition training and minimal additional hardware.
RAM allows analysis to occur the first response of an acquisition and enables RAM to view the data of an static evidence item to which duplicate validation techniques can be applied [3].
The necessity of analysis has been demonstrated by reiterate the weaknesses in forensic computing methodologies, tools and techniques.
Digital evolution progresses are the challenges to forensic investigators are to be expanded. The number and capacity of devices, network connectivity and bandwidth, are potential for the use of anti-forensic techniques. There are also other challenges in the collection and analysis of devices technical challenges, such as the moving of data storage to off-site systems [4].
Forensic computing needs to collect the challenges with tools, techniques and processes to understand the digital evidence and to detect and analyses the systems where these are utilized. Present tools and techniques in memory forensics are need to expand the low level analysis. The tools and techniques of an high level data of applications and technologies are for typical forensic computing methodologies.
The acquisition of an physical memory was verified to the various levels by comparing MD5 hashes. The time taken to produce the memory dumps of physical hardware was found to be significantly longer than on simulated hardware.
Uncertainty if the input for imaging is actually the RAM as malware cane be utilised to prevent RAM access or incorrect representation of RAM to prevent detection.
Analysis assumptions on process structure’s doubly linked list does not take unlinked ones such as old and hidden processes into account
RAM in certain cases can be present in spite of loss in power supply up to certain periods of time. Hence, its volatility comes into question.
7.1 LIVE FORENSICS ANALYSIS WORKFLOW
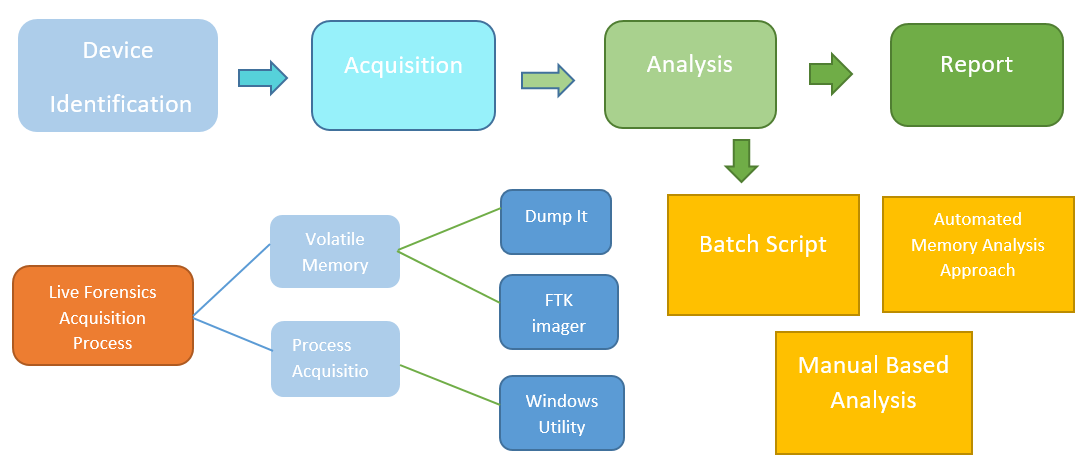
Figure 2: live forensics workflow
- MEMORY FORENSICS
Memory Forensics is a procedure to captures the memory dump, and list the analyses of an information obtained from systems memory. Numerical analysis is used to collect the volatile data of evidence in practical time.
Data captured from memory dump is further analysed in forensic laboratory. It was loaded into a memory when user types the password, or when data is going to be decrypted [9].
The passwords and keys are necessarily loaded and stored in memory. Analysis of the memory can allow Techniques and
Tools for Recovering and Analyzing Data from Volatile Memory to recover. Traditional analysis is that the inability of the physical disk to reveal information about processes that were running in memory.
The investigator intuition how the utilization were being used on the system of attack. It is possible for a open the hide data in memory who has negotiate a system to store data on the system’s drive.
- Viruses and Worms exist in memory that’s why Forensics analysis is hard to perform as the malicious activities couldn’t be captured.
- Forensics evidences are extracted from volatile memory which reside in system.
- Examination of activities such as login, internet, usage history uninstalled programs, deleted files can be found in volatile memory.
- Network information of currently logged on user, processes and services can be found in volatile memory.
Carrying out a Memory Forensics investigation will require in-depth knowledge of the most recent trends in the field. Here are the six main stages that an investigation should cover:
- Identifying the rogue processes posing as legitimate processes by heuristic methods
- Detecting anomalies in the treatment of objects being processed (DLLs, Registers, Threads, etc.),
- Examining the network artefacts and the communication ports used by the processes of the system in memory to determine the suspect elements;
- Searching for evidence of code injection and methods of obfuscation
- Searching for signs of the presence of a rootkit by the hooking detection method;
- Making a copy of the process in memory and the drivers of the suspect system
- ARCHITECTUTRE:
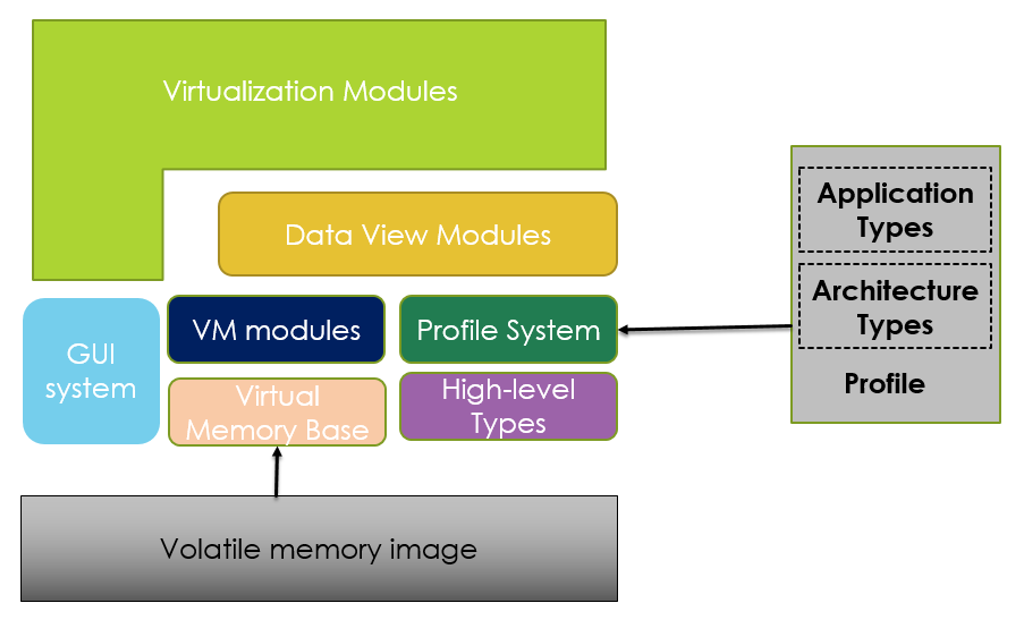
Figure 3: Live forensics architecture
- Visualization Modules contains two modules: Object Browser and Address Space Viewer.
- Object Browser will interpret the memory at abstraction level with the support for applications
- Address Space viewer will visualize the data which appears in virtual or physical address space.
- Virtual Memory Base and Modules will simulate to the random access of data and support to identify whether given data is accessible in memory.
- High level types contains objects which are an abstraction of data that was found in a Virtual Memory. Objects will have a Deep Member Access which provides a mechanism for the investigator to reference data. Allows a digital forensic investigator to perform objects operations in memor.
- Data View Modules Views the abstractions on address space and generally use profiles of a specific application that are present in address space.
- Data Analysis Modules Provides investigator with the potential to record and automate the tasks in data
- By using GUI Investigator will navigate and organize the data that are more likely to have the success at the time of investigation.
- FORENSIC EVIDENCE COLLECTION
The memory is assigned to the application in the investigation of an extracted image captured. Strings are used to extract the text information from memory dump. Pattern matching is used to identify the precedent of user activity and approach takes the user input and test the image with the extracted memory dump.
The remnant of the user text the extracted information from the memory dump. The user input was stored on the applications of a user input and the data is retrieved from the volatile memory analysis of a Windows computer systems. The probe is focused on the information related to the user that application was recovered when the memory is grab at running application.
- TOOL IMPLEMENTATION
The automation tool used for analysis. The following plugin was utilised for obtaining the Profile which is necessary for executing further plugins:
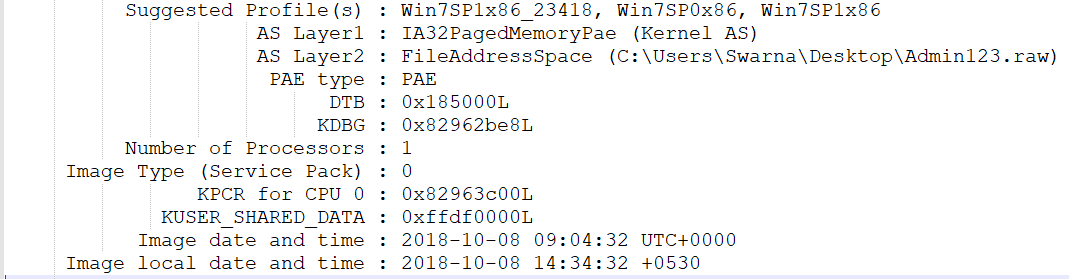
Screenshot 1: List of profiles in memory dump
11.1 DLLLIST
To view all the DLL’s loaded by a process we use the plugin dlllistto verify if the process is calling its related DLL. It can be executed using the following plugin:
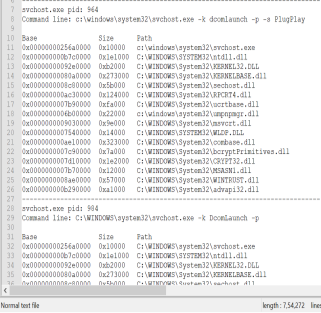
Screenshot 2: DLL’s loaded in process
11.2 HANDLES
Handles will display the handles which are opened in a process and it applies to files, registry keys, and mutexes, named pipes, events, window stations, desktops, threads, and all other types of executive objects.
Screenshot 3: Handles in process
11.3 PSGETSIDS:
To view the Security Identifiers which is associated with a process. It identifies processes like malignant exemption and specific users.
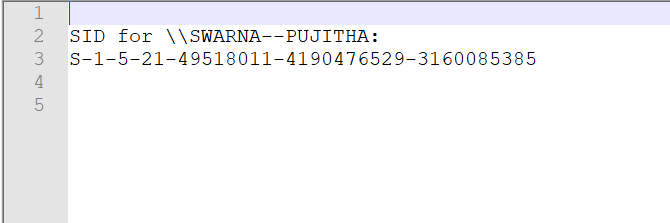
Screenshot 4: Security identifiers
11.4 PSINFO
PSINFO will gather the processes of a Virtual Address Descriptor and Process Environment Block information and displays the suspectable memory areas for running system.
Screenshot 5: Process information
11.5 PSLIST
Pslist is a plugin used to obtain a list of processes running during imaging and provides information like process name, PID, PPID, threads, start and end time of process.
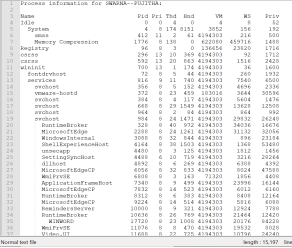
Screenshot 6: List of Process
11.6 PSLOGGEDON
PSLOGGEDON can view the loaded profiles of a logged on users in the registry. It displays the locally logged users and logged users through local or remote computer [5].

Screenshot 7: Logged on users
11.7 CONSOLES
Consoles will find the commands in command prompt that attacker was typed and it scans the console information rather than command prompt. It collects the entire screen buffer and it displays the information like files, directories listed in directory command.
Screenshot 8: List of commands in command prompt
11.8 TCPVCON
It displays the list of all TCP and UDP endpoints of a system in local and remote addresses of TCP connections. It reports processes names and subset of netstat in windows.
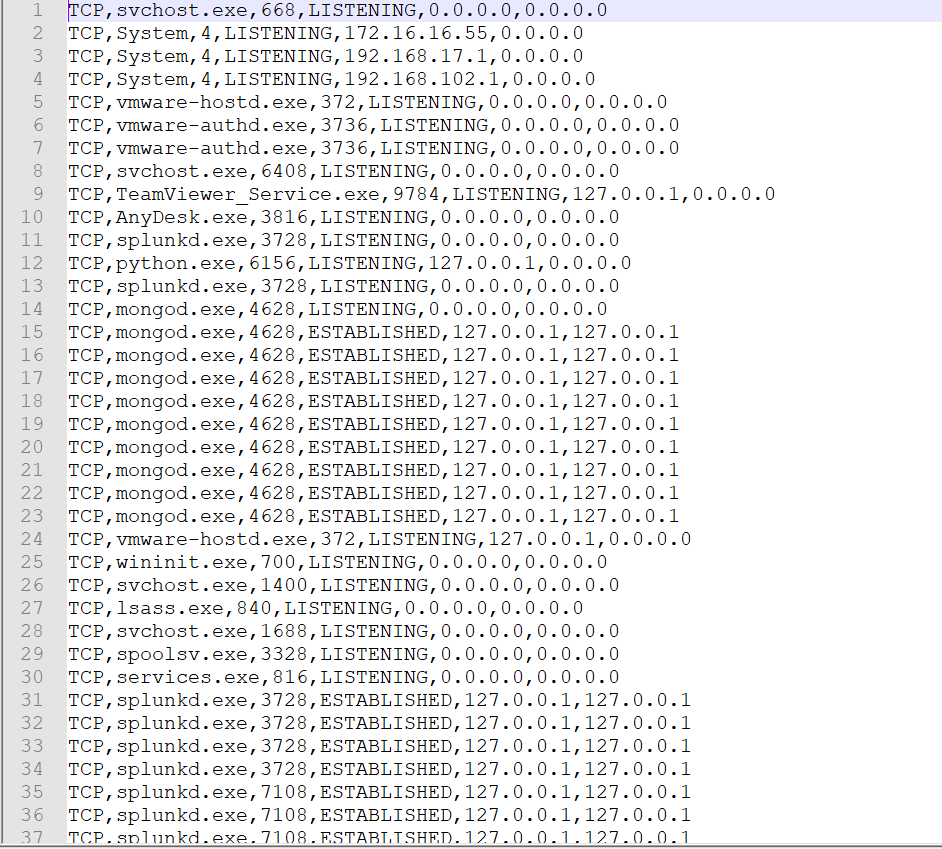
Screenshot 9: TCP details
- ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This work is supported by the Department of Science and Technology, India through the fund sanctioned for improvement of Science & Technology infrastructure, at department of CSE, K.L University, by order number SR/FST/ESI-332/2013.
- CONCLUSION
In traditional digital forensics, when an incident has occurred the forensics investigator will identify the incident and perform forensic analysis to find the root cause of crime. Now-a-days digital forensics has developed in such a way that live monitoring is the main perspective to identify and mitigate the incident that happened. Live monitoring provides an in-depth analysis of identifying how the incident happened and what are the activities occur while the system is active. It’s complicated to acquire a memory dump and perform the volatile analysis using the command line. So, to make it easier for analyzing the dump, the approach in this paper represents the automated analysis.
14. REFERENCES:
- Victor Voelzow “LIVE DATA FORENSICS – OR – WHY VOLATILE DATA CAN BE CRUCIAL FOR YOUR CASES” Blog on council of Europe Apr 30, 2013.
- Mahesh Kolhe, Purnima Ahirao “LIVE VS DEAD COMPUTER FORENSIC IMAGE ACQUISITION” International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technologies, Vol. 8 (3), 2017, 455-457, ISSN: 0975-9646.
- Lei Zhang, Dong Zhang, Lianhai Wang “LIVE DIGITAL FORENSICS IN A VIRTUAL MACHINE” International Conference on Computer Application and System Modeling 2010 Vol 4, 978-1-4244-7237-6.
- C.L.T. Brown “COLLECTING VOLATILE DATA” Lecture Notes on Digital Forensics Aug 27, 2006.
- Online “live-response-collecting-volatile-data-windows-forensic-analysis” tutorial on windows forensics analysis.
- Pooja Gupta “CAPTURING EPHEMERAL EVIDENCE USING LIVE FORENSICS” IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering, e-ISSN: 2278-2834,p- ISSN: 2278-8735, PP 109-113.
- Brian Hay, Matt Bishop, Kara Nance “LIVE ANALYSIS: PROGRESS AND CHALLENGES” IEEE Xplore, 10.1109/MSP.2009.43, 2009.
- Marthie Lessing, Asie Von Solms “LIVE FORENSIC ACQUISITION AS ALTERNATIVE TO TRADITIONAL FORENSIC PROCESSES” Research Gate, 30511418, 2008.
- Martha Maria Grobler “LIFORAC – A MODEL FOR LIVE FORENSIC ACQUISITION” UJ Content UJ Institutional Repository, 2009.
- Esan P. Panchal “EXTRACTION OF PERSISTENCE AND VOLATILE FORENISCS EVIDENCES FROM COMPUTER SYSTEM” International Journal of Computer Trends and Technology, V$(5):964-968, May Issue 2013, ISSN 2231-2803
- K.V.D.KIRAN,” MULTI CROSS PROTOCOL WITH HYBRID TOPOGRAPHY CONTROL FOR MANETS”, Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, 2017. Vol.95. No.3, ISSN: 1992-8645
- K.V.D.KIRAN,”IntegratedDistributed Architecture to Integrate Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) with Grid for Healthcare,” International Journal of Bio-Science and Bio-Technology”, Vol.7, No.3 (2015), pp.243-250, ISSN: 2233-7849 IJBSBT.
- K.V.D.KIRAN,”A Critical study of information security risk assessment using fuzzy and entropy methodologies,” International Journal on Computers and Communications”, Pages: 17-22,Vol1,Isuue1,Dec-,12, ISSN: 2319 – 8869.
- K.V.D.KIRAN,” “Literature Review on RisK Literature Review on Risk and their Components”International Journal for Research in Emerging Science and Technology (IJREST) “,Volume-1, Issue-6, November 2014”,(e-ISSN 2349-7610).
- K.V.D.KIRAN,”Performance Analysis of Layered Architecture to Integrate Mobile Devices and Grid computing with a resource scheduling algorithm”, IEEE CS’07, SIVAKASI, TAMIL NADU,India
- K.V.D.Kiran “Risk Assessment in Distributed Banking System,” International Journal of Applied Engineering Research(IJAER)”, ISSN 0973-4562 Volume 9, Number 19 (2014) pp. 6087-6100
- K.V.D.Kiran ,”Analysis and Classification Scheme of Risk Assessment Miniatures placed on Different Criteria for Reducing the Risk”, International Journal of Applied Engineering Research”pp.12069-12085, ISSN 0973-4562 Volume 9, Number 22 (2014)
- K.V.D.Kiran ,”Information Security risk authority in critical informative systems”,CSIBIG 2014
- K.V.D.Kiran ,”Survey on mobile malware analysis and detection”, Volume 7, Issue 2.32 Special Issue 32, 2018, Pages 279-282, ISSN:2227524X
- K.V.D.Kiran ,”Authorization of data in Hadoop using Apache Sentry”, Volume 7, Issue 3.6 Special Issue 6, 2018, Pages 234-236, ISSN:2227524X
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal



